The power of relative strength as a return factor has been well documented and that evidence is the reason that relative strength drives all of our investment strategies. However, just because it is a winning return factor over time doesn’t mean that anyone should or will construct an asset allocation composed entirely of relative strength-based strategies. Financial advisors who are in a position to decide which strategies to include in an asset allocation must then decide how to find complementary return factors. We have previously written about the benefits of combining relative strength and value, for example.
However, it appears that value is not the only suitable complement for relative strength strategies. Another option would be to consider combining the recently introducted PowerShares S&P Low Volatility Portfolio (SPLV) with our own PowerShares DWA Techical Leaders Portfolio (PDP).
A description of each is as follows:
The PowerShares DWA Technical Leaders Portfolio (PDP) is based on the Dorsey Wright Technical Leaders™ Index (Index). The Fund will normally invest at least 90% of its total assets in securities that comprise the Index and ADRs based on the securities in the Index. The Index includes approximately 100 U.S.-listed companies that demonstrate powerful relative strength characteristics. The Index is constructed pursuant to Dorsey Wright proprietary methodology, which takes into account, among other factors, the performance of each of the 3,000 largest U.S.-listed companies as compared to a benchmark index, and the relative performance of industry sectors and sub-sectors. The Index is reconstituted and rebalanced quarterly using the same methodology described above.
The PowerShares S&P 500® Low Volatility Portfolio (SPLV) is based on the S&P 500® Low Volatility Index (Index). The Fund will invest at least 90% of its total assets in common stocks that comprise the Index. The Index is compiled, maintained and calculated by Standard & Poor’s and consists of the 100 stocks from the S&P 500 Index with the lowest realized volatility over the past 12 months. Volatility is a statistical measurement of the magnitude of up and down asset price fluctuations over time.
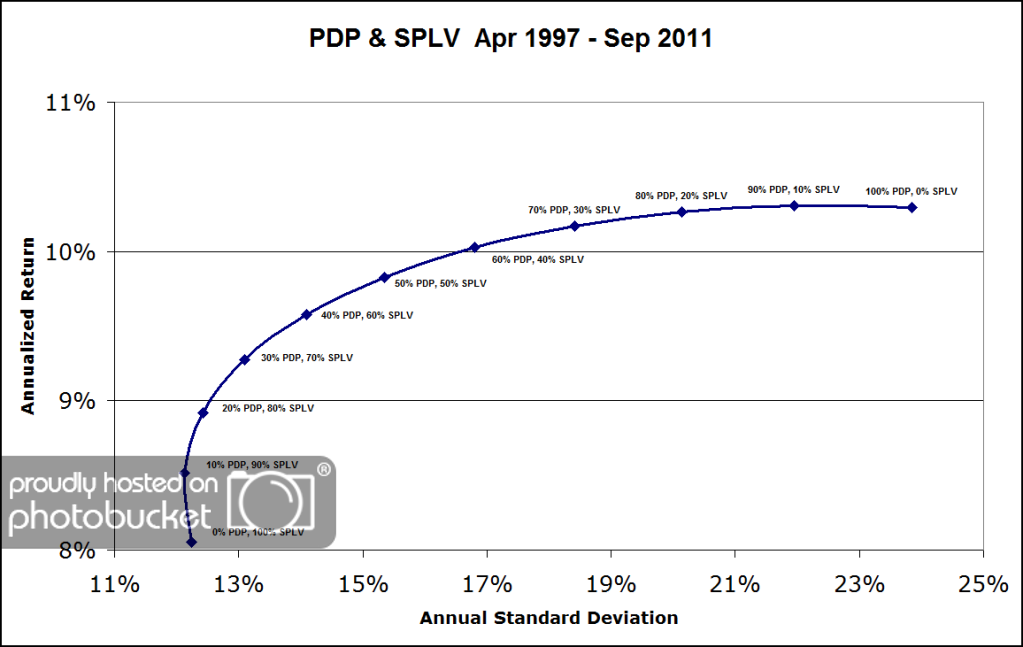
The efficient frontier below points out that combining the two can be an effective way to reduce the volatility and/or increase the return over using PDP or SPLV independently.
(Click to enlarge)
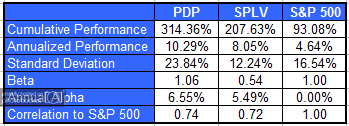
The table below is also for the period April 1997-September 2011. (The hypothetical returns for PDP only go back to April 1997.)
Perhaps most interesting to asset allocators is the fact that the correlation of excess returns of PDP and SPLV over this time period was -0.29. The goal of asset allocation is to not only add value, but to also construct an allocation that clients will stay with for the long-run. Rather than whip in and out of PDP, perhaps a more enlightened approach is to buy and hold positions in both PDP and SPLV for a portion of the allocation.
For the time periods when hypothetical returns were used, the returns are that of the PowerShares Dorsey Wright Technical Leaders Index and of the S&P 500 Low Volatility Index. The hypothetical returns have been developed and tested by the Manager (Dorsey Wright in the case of PDP and Standard & Poors in the case of SPLV), but have not been verified by any third party and are unaudited. The performance information is based on data supplied by the Dorsey Wright or from statistical services, reports, or other sources which Dorsey Wright believes are reliable. The performance of the Indexes, prior to the inception of actual management, was achieved by means of retroactive application of a model designed with hindsight. For the hypothetical portfolios, returns do not represent actual trading or reflect the impact that material economic and market factors might have had on the Manager’s decision-making under actual circumstances. Actual performance of PDP began March 1, 2007 and actual performance of SPLV began May 5, 2011. See PowerShares.com for more information.








This is interesting, and something very easy to implement. How about a chart summarizing the actual combined strategy performance across the curve, including CAR and max DD metrics?
[...] of the big advantages of factor exposure is that some factors offset one another beautifully. We’ve written before about the nice efficient frontier that is created by combining relative s…. (You can see the chart below.) These factors work well together because the excess returns are [...]